
Architectural Innovations for Smart Homes
Architectural Innovations for Smart Homes
As technology continues to evolve, it has significantly impacted how we design and live in our homes. The concept of the smart home — a home equipped with internet-connected devices and systems that can be controlled remotely — has moved from science fiction to reality. Today, architects are integrating smart technologies into their designs, enhancing comfort, security, and energy efficiency. This article explores the architectural innovations that are enabling smart homes and creating a more connected living environment.
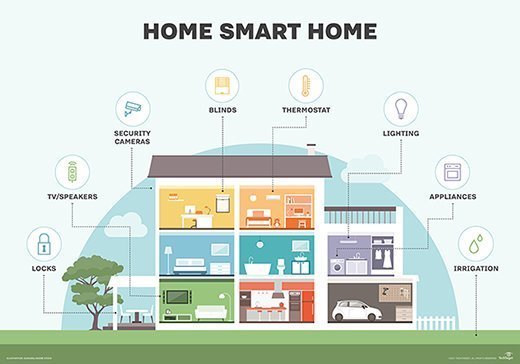
The Rise of the Smart Home
A smart home is a living space that uses interconnected devices and systems, such as lighting, heating, cooling, security, and entertainment, to improve the quality of life for its occupants. These systems can be controlled through smartphones, voice assistants, or automated processes, offering a level of convenience and customization that was once unimaginable.
Architects have recognized the potential of integrating smart technology into home design. By incorporating advanced technologies into the architectural structure, designers can create more efficient, secure, and user-friendly living spaces. The fusion of architecture and technology allows for a seamless experience that enhances both the functionality and aesthetic appeal of a home.

Smart Home Integration into Architectural Design
One of the key challenges in designing smart homes is ensuring that technology is integrated in a way that doesn’t disrupt the home’s aesthetics or functionality. Architects are using several innovative techniques to achieve this, ensuring that smart systems are not only efficient but also blend naturally into the home’s design.
Invisible Infrastructure
One of the first steps in integrating smart technologies into a home is creating the infrastructure that will support these systems. Modern homes often incorporate invisible infrastructure, such as wiring, sensors, and networks, hidden within walls, ceilings, and floors. This allows for a cleaner, more minimalist aesthetic without sacrificing functionality. For example, smart lighting systems and sound systems can be embedded into walls or ceilings, creating a sleek, modern appearance while providing high-tech convenience.
In many cases, architects are also designing homes with future-proofing in mind. This means building infrastructure that allows for easy integration of new technologies as they become available. Smart homes are designed with adaptable spaces and hidden conduits, ensuring that the home can evolve as technology advances.
Open-Plan Designs for Seamless Technology
Open-plan designs, which have been a popular trend in architecture for years, work particularly well with smart home technologies. Large, open spaces allow for seamless integration of smart devices, such as thermostats, lighting systems, and security cameras, without cluttering the environment with visible technology. Smart home features can be controlled with voice commands or apps, making it easier to manage the space without the need for bulky switches, knobs, or devices.
For example, smart lighting systems can automatically adjust to the time of day or the presence of people in a room. This means that homeowners don’t need to manually adjust light switches or worry about energy wastage. The architecture of an open-plan home supports these systems, with sensors and control panels hidden from view, creating a smooth, unobtrusive look.
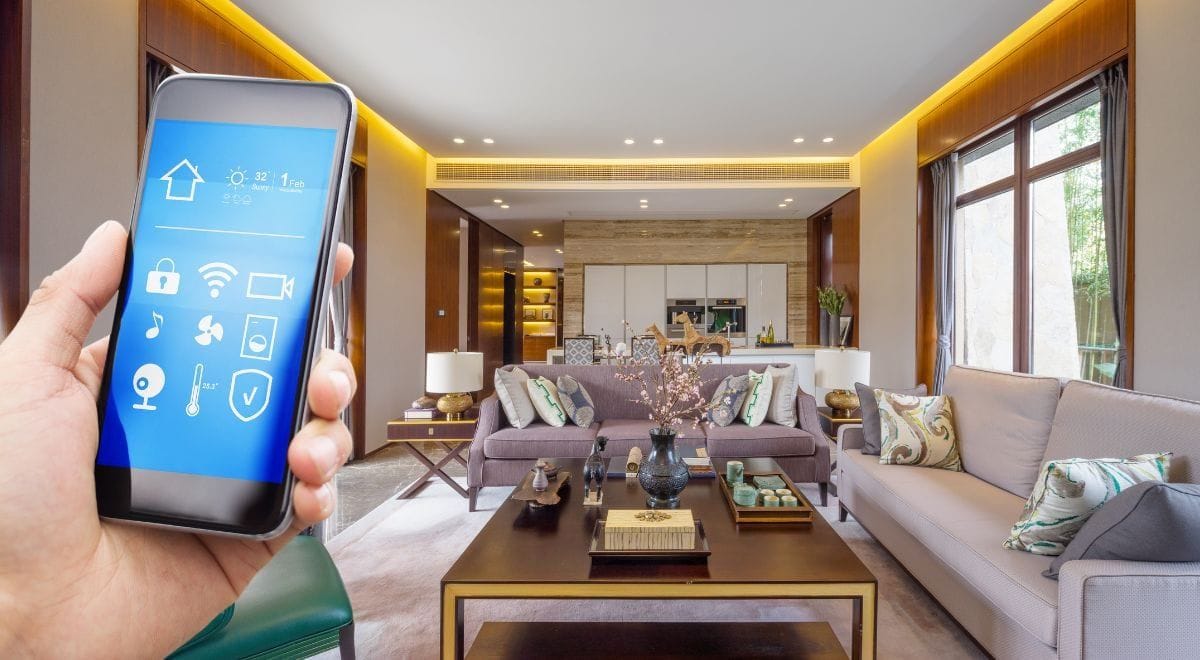

Built-in Smart Features
Some smart technologies are now being built directly into the architecture itself. For instance, smart glass can be used in windows and walls to control privacy and temperature. This glass can automatically darken when exposed to sunlight, reducing heat gain and improving energy efficiency. Additionally, built-in smart speakers, like those from Amazon or Google, can be incorporated into walls or ceilings, offering hands-free control of various systems within the home.
Another example is the integration of smart heating and cooling systems into the architectural design. Programmable thermostats, sensors, and smart HVAC systems can be built into a home’s framework, allowing for precise control of temperature and airflow. These systems can be programmed to respond to individual preferences or the time of day, creating a more energy-efficient and comfortable environment without the need for separate, visible thermostats or vents.
Sustainability and Smart Home Architecture
In addition to enhancing convenience and comfort, smart home technologies also contribute to sustainability. Many modern homes are designed with a focus on energy efficiency, and smart technologies play a vital role in reducing a home’s environmental impact. For example, smart thermostats help regulate temperature by learning the homeowner’s habits and adjusting the heating and cooling systems to avoid energy waste.
Architects are increasingly designing homes with solar panels, energy-efficient windows, and smart grids to create more sustainable, self-sufficient homes. Solar energy can be harnessed through the roof or exterior of the building, and smart technologies can optimize energy use, storing excess energy for later use. This reduces reliance on external energy sources and lowers the home’s carbon footprint.
Furthermore, rainwater harvesting systems and smart irrigation systems are being incorporated into the design to promote water conservation. Smart sensors in the garden or lawn can detect moisture levels and adjust irrigation schedules to prevent overwatering, helping homeowners save water and reduce utility costs.
Home Security and Smart Systems
Smart home security systems are among the most popular applications of smart technology in residential architecture. Smart doorbells, cameras, motion sensors, and locks can be easily incorporated into a home’s design without disrupting the aesthetic. For instance, cameras can be discreetly installed in door frames or integrated into the architecture of the building.
Smart security systems offer a level of control and monitoring that traditional systems cannot match. Homeowners can monitor their property remotely, receive real-time alerts, and control security features such as locks and alarms through their smartphones. These systems can also be programmed to work together with other smart home devices, such as lighting and heating systems, to create a safer and more secure environment.
Smart Kitchens and Bathrooms
The integration of smart technology in kitchens and bathrooms is another area where architectural innovation plays a key role. In modern kitchens, smart refrigerators can monitor food inventory, suggest recipes, and even order groceries. Smart ovens and cooktops can be controlled remotely, ensuring that meals are cooked perfectly every time. These appliances can be built seamlessly into the cabinetry and countertops, creating a clean, organized space.
In the bathroom, smart showers and automated faucets are designed to conserve water while providing a luxurious experience. These systems can be programmed to adjust water temperature, pressure, and flow based on personal preferences. Touchless faucets and smart mirrors with built-in lighting and voice assistants are also becoming more common, providing convenience and reducing the spread of germs.
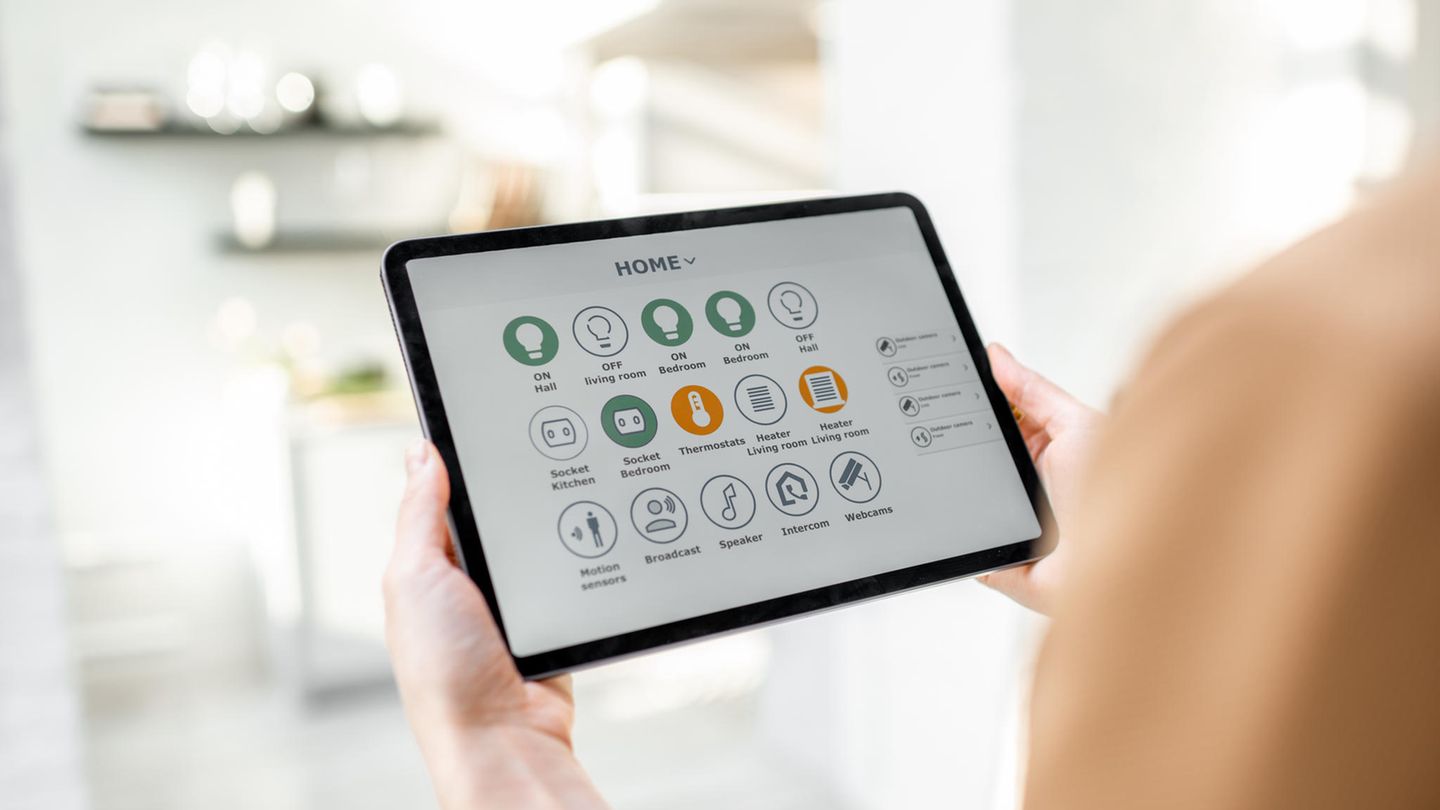

Conclusion
Architectural innovations for smart homes are transforming the way we design and live in our homes. By seamlessly integrating smart technologies into the structure of the home, architects are creating living spaces that are more efficient, sustainable, and user-friendly. The future of home design is undoubtedly going to be even more connected, with technology becoming an integral part of the home’s architecture. As these innovations continue to evolve, smart homes will become more accessible and functional, offering a level of comfort and convenience that makes modern living more enjoyable and efficient.











